Identifying Fake News Using BERT and GPT-2
This is our final project for our Natural Language and Processing class in collaboration with Adriane Amorado, Tonichi Edeza and Ethan Casin
Summary
Increasing internet penetration and smartphone use has made the spread of misinformation much easier than ever before. Countries like the Philippines are particularly susceptible due to the lack of technological safeguards, brought on by Filipino being an unsupported, low resource language in the tech world. In finding a cost-effective way of filtering fake news, we run a comparative analysis of BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) and GPT-2 Model trained on a fake news data.
The dataset used contains 6,459 Tagalog news articles released in the year 2020, each labeled real or fake. Some of these articles have both English and Tagalog content. Fake news articles were scraped from online sites that were tagged as fake news sites (PinasLatestNews, NoypiAko , CitizenExpress) by the media fact-checking organization Verfiles. The data was manually curated based on features such as disclosure of author, disclosure of sources, transparency of the publisher, and integrity of website. On the other hand, real news articles were gathered from mainstream news websites in the Philippines such as Bandera and PhilStar.
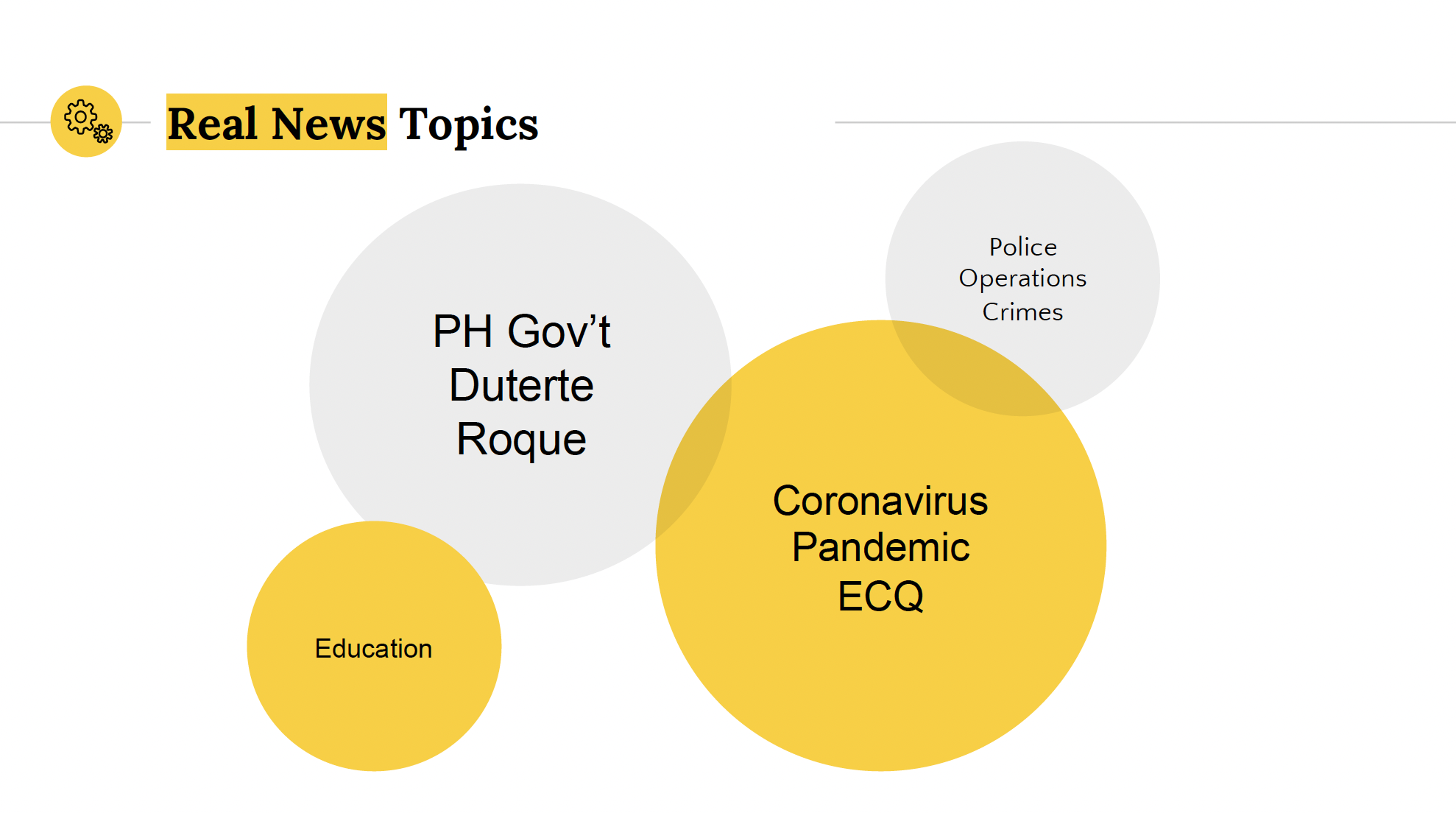
Applying LDA on the dataset with 10 topics and 100 passes, we were able to identify key topics in both legitimate and fake news classes. Fake and legitimate news sites generally discuss common topics in the Philippines. However, fake news sites topic mainly centers on political figures.

Although the dataset is highly imbalanced (with 4,041 real and 2,418 fake news), both models were able to score 82% on the testing data. This can still be improved by using a more balanced dataset, working with a pre-trained bilingual model,and lastly by using a multiclass model.
Keywords: BERT; GPT-2; Fake News Detection


